Titanium base abutments have increasingly been utilized in implant dentistry due to their strength, durability, and biocompatibility. Dental professionals need to be aware of the potential for issues. This includes screw loosening and excess cement around the implant soft tissue that can occur with titanium base abutments. Through advancements made in digital workflow technology combined with CAD/CAM fabrication processes these titanium products are becoming more precise which is adding to improved satisfaction from patients on a longer-term basis.
As research continues to optimize the use of titanium-based abutments, patients and dental professionals need to remain informed to achieve successful outcomes.
What is the Titanium Base Abutment?
Titanium base abutments serve as an essential connection between dental implants and their restorations. Using titanium implants with their corresponding base abutments provides the needed support for various restorations. This blog discusses the advantages and types of Ti-base abutments. It also discusses the customization of the titanium base abutment using CAD/CAM technology, soft tissue management, and indications.
Advantages of the Titanium Base Abutment
Titanium is a highly favored material when it comes to dental implant abutments, due to its superior mechanical properties, and biocompatibility. Its exceptional features include robustness, high tensile strength, low density, and good osseointegration capabilities. The Ti-Base abutment also provides excellent corrosion resistance that grants longevity to the item. Therefore, titanium is an optimal choice for any type of implant-related restoration.
Dentists seek Edison Medical’s leading titanium-based solutions as human tissue has no ill reaction with this material. Moreover, our Ti-Base solutions offer higher durability and fracture resistance, making them stand out against other available titanium abutments.
Edison Medical’s Titanium Base Abutment
Our Ti-Base abutments ensure compatibility with advanced digital technology. Dentists can now craft customized implants for patients with unparalleled precision. Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) utilize sophisticated software to design and manufacture implant prosthetics. With CAD/CAM, there is no more patient discomfort caused by impressions, no need for retakes, and no stress for the dentist.
At Edison Medical™, we are committed to offering top-notch, technologically advanced products. Experience the future of dentistry with our Ti-Base abutments and restoration products – available for purchase now!
Types of Ti-Base Restorations
Crowns that are built using titanium-based restorations come in two primary varieties: screw-retained and cement-retained.
Screw Retained Restorations
In a screw-retained abutment system, the abutment is attached to the implant fixture using a screw. The abutment has a hole through which the screw passes and is tightened down onto the implant fixture. The screw retains the abutment in its position. The design allows easy removal and replacement of the abutment. Therefore, it is a popular choice for implant-supported restorations.
Screw-retained abutments are often used when easy retrievability and potential future maintenance or adjustments are important considerations. They are commonly made from titanium for their biocompatibility and strength. Moreover, they eliminate the risk of residual cement, which can cause peri-implantitis.
Cement Retained Restorations
In a cement-retained abutment system, the abutment is screwed onto the implant as the restoration is cemented over the abutment. This method offers more aesthetic results as there is no visible screw hole on the restorations. However, it can be challenging for dental professionals at clinics to notice the tiny particles of the excess cement. It is risky as the excess cement can reach the implant, consequently causing implant failure.
Prefabricated Abutment vs. Custom Abutment

Prefabricated titanium base abutments have high fracture resistance and maintain the stability of surrounding tissue. They are compatible with multiple systems. However, they are suitable only for specific cases, such as cement-retained restorations and situations with ideal implant placement, depth, emergence profile, and diameter of the area of missing teeth.
It is preferable to use custom titanium base abutments to address the limitations of prefabricated abutments. Especially in off-axial implants where the screw access emerges buccally. Custom abutments can be either cast from metal alloys or milled using CAD/CAM technology. They offer high strength, durability, and the option for either cement-retained or screw-retained prostheses. They also allow the fabrication of fixed prostheses with appropriate thickness.
Moreover, custom-made titanium base abutments provide a precise fitting process, improved soft tissue management, and increased durability due to extraoral cementation.
Zirconia Abutment VS Titanium Abutment
Zirconia abutments, crafted from zirconium dioxide, offer a natural appearance and strength. They have a natural tooth color, making them aesthetically superior especially in visible areas. However, they demand expertise for adjustments. Although less flexible than titanium, they provide a visually appealing solution for patients seeking beauty and durability.
Titanium abutments are more biocompatible and stronger than zirconia and ceramic abutments. They allow precise adjustments tailored to individual needs. Despite lacking natural tooth color, they are discreet under crowns, making them a budget-friendly choice, often chosen for their reliability.
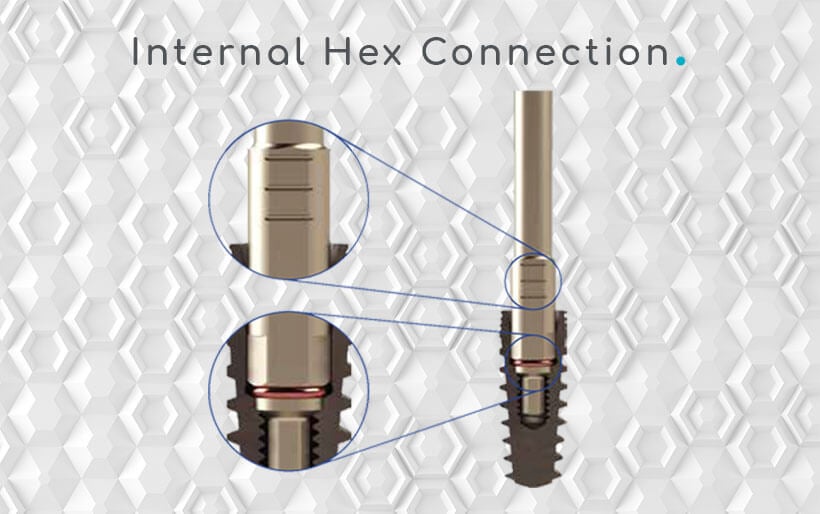
Internal Hex and Titanium Base Abutment
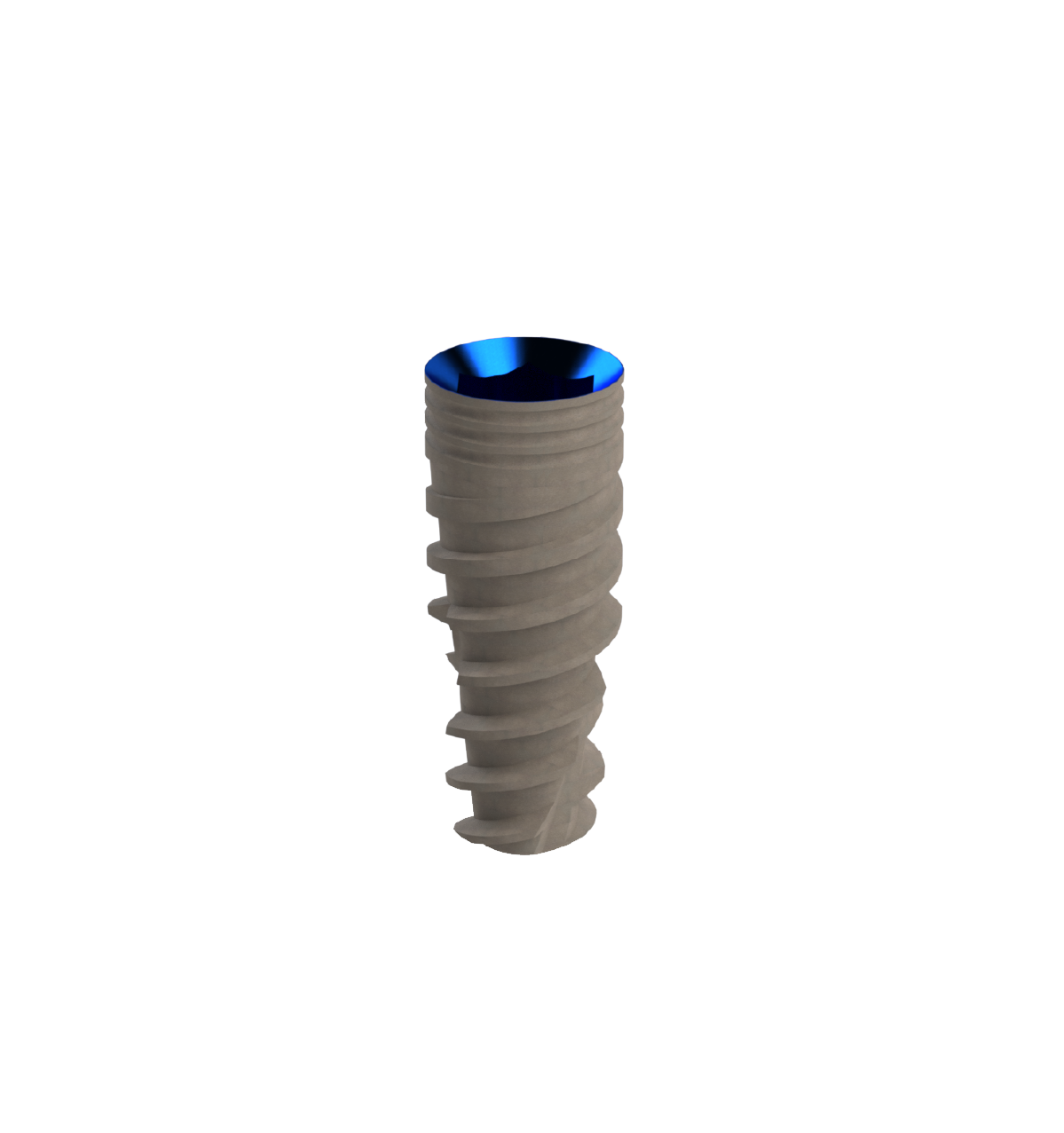

The internal hex refers to the type of connection between the implant fixture and the titanium metal abutment. The internal hexagon is a specific geometric feature inside the implant fixture onto which the abutment is attached. The internal hex design provides mechanical stability and prevents rotation of the abutment. Consequently ensuring a secure connection between the implant and the restoration. The titanium base is customized to have an internal hexagon that matches the internal hex feature in the implant fixture. This precise fit ensures a strong and stable connection, allowing the abutment to be securely attached to the implant.
Benefits of CAD/CAM Technology in Ti Base Abutments
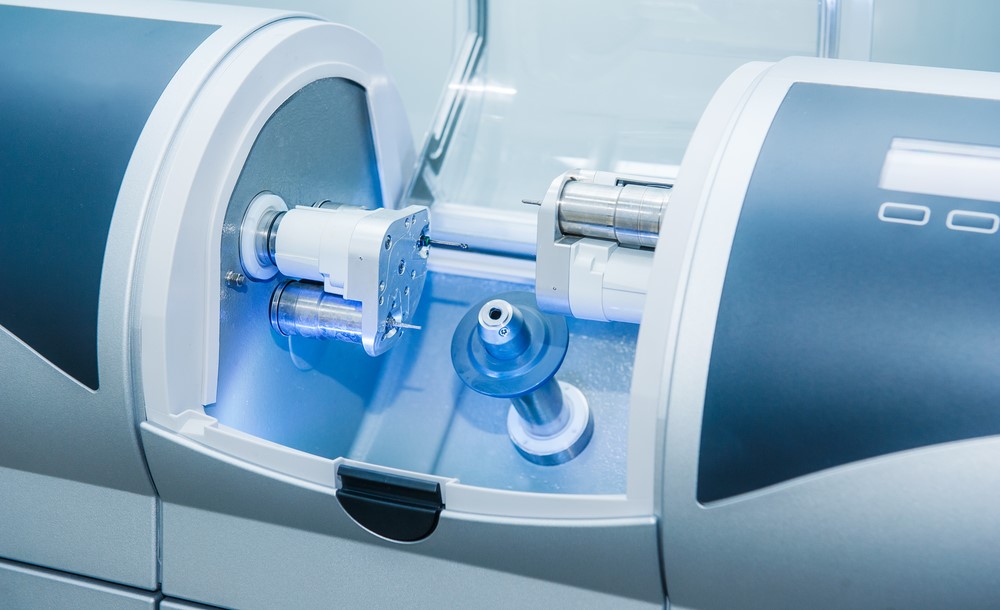
CAD/CAM technology makes it easier for dentists to deliver precise implant procedures and accurate fabrication for a precise fit with restorations. Therefore, fewer errors happen during operations due to the improved precision which allows a higher standard of patient care.
With CAD/CAM technology, dental professionals can create customized titanium base abutments. The customization process is done through virtual design, milling, and soft tissue optimization with biocompatible materials like titanium. This offers an unparalleled level of accuracy in production processes that are less prone to errors or inconsistency. Leading to better fitting implant-supported restorations for maximum patient satisfaction.
This technique significantly reduces both chairside time and traditional multiple appointments. Consequently, this results in much greater efficiency among dental professionals for a more favorable overall experience for patients. Therefore, CAD/CAM engineering has become important in contemporary implant dentistry.
Managing Peri-Implant Soft Tissue with Titanium Base Abutments

Dental professionals need to understand the range of methods and approaches available when managing peri-implant soft tissue with titanium base abutments. Appropriate treatment will encourage healthy tissue integration thus avoiding any infection, bone loss, or inflammation complications. Titanium bases are key in ensuring long-term stability and optimal aesthetics regarding these restorative measures. Therefore, their use not only guarantees proper peri-implant soft tissue management but also safeguards patients against unwanted effects.
To properly manage the soft tissue around titanium base abutments, dental professionals conduct regular evaluations to check for inflammation. Dental professionals may also employ augmenting techniques such as access flap surgery or regenerative procedures. Moreover, selecting the right type of abutment and ensuring proper placement are important steps in the effective management of these structures. Timing plays an important role during the implant restoration process when managing a patient’s peri-implant soft tissues. Hence it would benefit the patient more if the dental professional initiates this procedure at tooth extraction rather than after the implant placement. This is to ensure optimal healing and longer-term health overall.
Indications and Common Ti Base Abutment Issues
Dental professionals should be aware of potential complications with titanium base abutments, such as screw loosening and extra cement. It is important to understand the indications of these problems to ensure successful fixed implant restorations.
Preventing and Managing Screw Loosening
Insufficient torque, micro-movement, and the effects of occlusal forces can all contribute to screw loosening in titanium base abutments. To prevent such issues, dental professionals should ensure that contact is properly centered when fitting an implant. Moreover, they should carefully flatten cuspal inclination. A minimum of 22Ncm on the torque must be observed while utilizing suitable antimicrobial lubrication. In addition to the proper technique for tightening screws through the screw access hole.
It is also important to recognize signs related to possible screw looseness. For instance, when patients report slight mobility or movement of crowns, or bubbles forming after removal. These are some red flags associated with potential issues around base abutments and need careful attention. By being aware and tackling any problems early enough, dentists have a greater chance of achieving successful, lasting results.
Dealing with Excess Cement and Esthetic Challenges
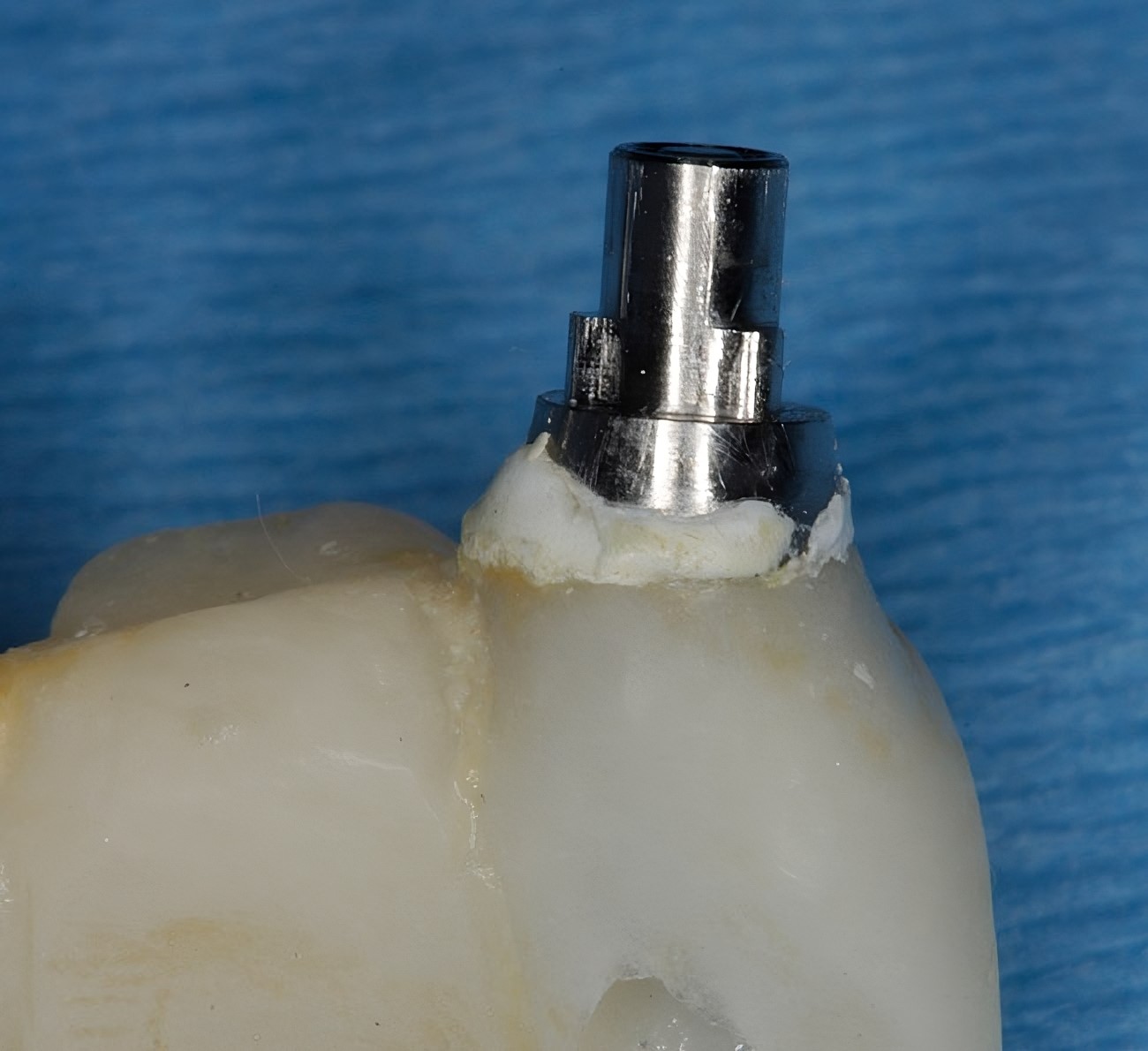
Excess cement causes marginal bone loss and peri-implantitis. To avoid such issues associated with titanium base abutments, dental professionals should use diamond burs or extra-oral cement removal techniques.
Customized abutment designs featuring larger surface areas for contact can lower the risk of problems related to material overloading. To achieve visually appealing outcomes with these abutments, it is important to manage soft tissue, customize colors, and design crowns effectively using ceramic or zirconia materials.